Why Pickles Last Longer Than Other Foods: The Science Behind Their Shelf Life
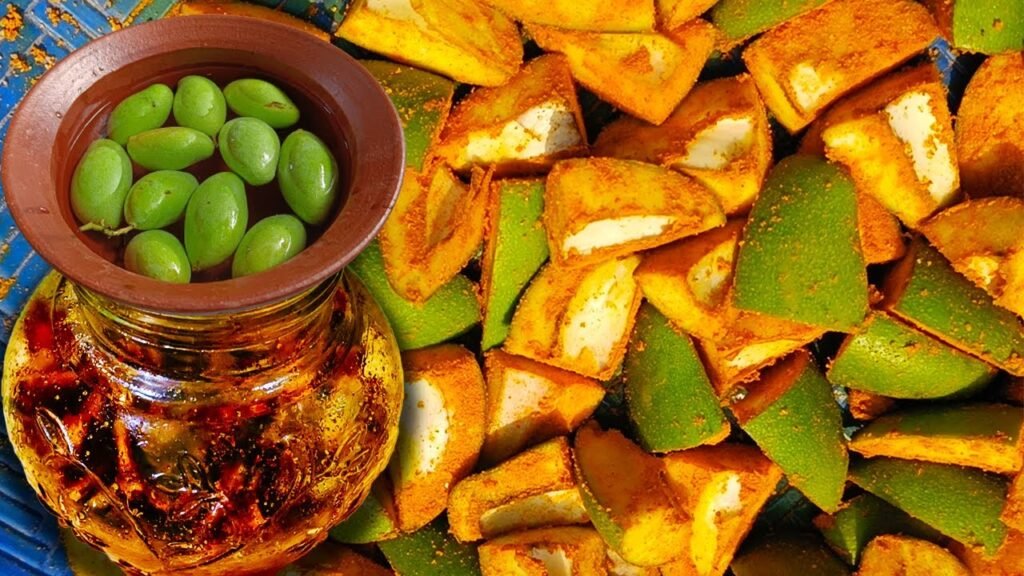

Pickles have been part of Indian kitchens for centuries – long before refrigeration or preservatives existed. While most foods spoil quickly, pickles remain fresh for months, sometimes even years, when stored properly.
So, what makes pickles different?
1. Natural Preservation Through Salt
How salt works:
- Draws moisture out of vegetables and fruits
- Creates an environment where bacteria cannot survive
- Slows down microbial growth
- Prevents spoilage naturally
High moisture = faster spoilage.
Pickles solve this with the right salt balance.

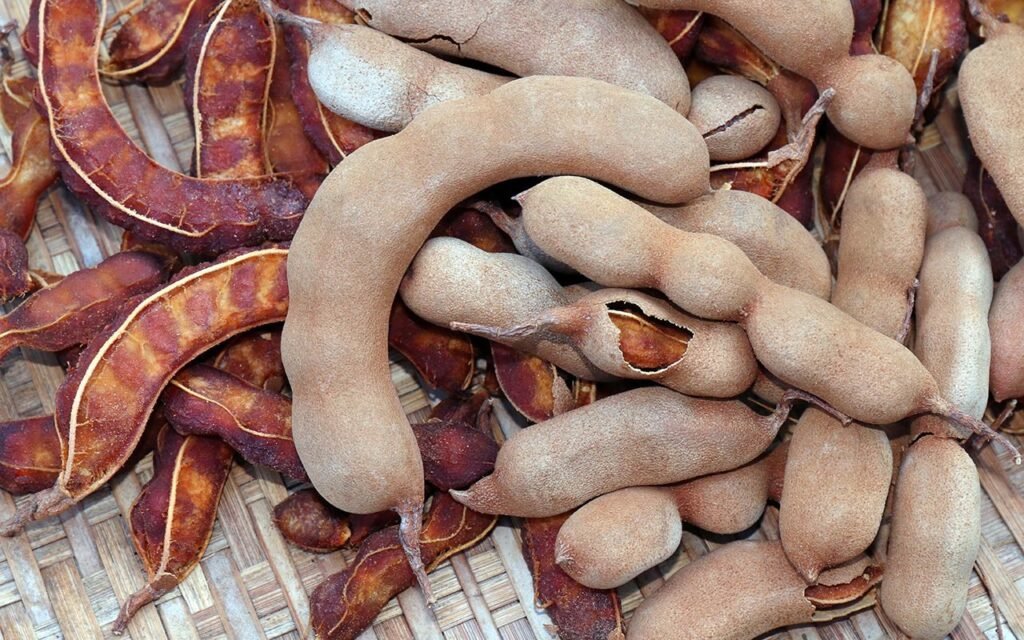
2. Acidity: The Power of Sour Ingredients
Pickles often use natural acidic elements such as:
- Lemon
- Tamarind
- Vinegar
- Raw mango
These acids:
- Lower pH levels
- Stop harmful bacteria from multiplying
- Act as natural food preservatives
This acidic environment is one of the main reasons pickles stay safe for long periods.

3. Oil Creates a Protective Barrier
Oil helps by:
- Forming a seal over the pickle
- Preventing air and moisture from entering
- Reducing oxidation
- Locking in flavor and freshness
Mustard oil, sesame oil, or refined vegetable oils are commonly used depending on regional style.

4. Spices with Antimicrobial Properties
Pickles are rich in spices that naturally fight bacteria.
Common examples include:
- Turmeric – antibacterial & antifungal
- Mustard seeds – antimicrobial
- Garlic – natural antibiotic
- Chilli – inhibits microbial growth
- Fenugreek – digestive & preservative
These spices work together to protect the pickle without artificial chemicals.
5. Low Water Activity
Most foods spoil because bacteria thrive in moisture.
Pickles:
- Have reduced free water content
- Are dehydrated partially using salt
- Are soaked in oil or acidic medium
This creates low water activity, making it difficult for microorganisms to grow.
6. Fermentation (In Some Pickles)
Certain traditional pickles undergo natural fermentation.
Fermentation:
- Produces beneficial acids
- Encourages good bacteria
- Suppresses harmful microbes
- Enhances flavor and shelf life
This process was widely used before modern preservation techniques existed.
7. Proper Storage Practices
Shelf life also depends on how pickles are stored.
Best practices include:
- Airtight containers
- Clean, dry spoons
- No moisture contamination
- Storage away from sunlight
When followed correctly, pickles remain safe and tasty for extended periods.


Why Pickles Outlast Most Foods (Quick Comparison)
Food Type | Shelf Life | Reason |
Fresh fruits | Few days | High moisture |
Cooked food | 1–2 days | No preservation |
Bread | Few days | Mold growth |
Pickles | Months–years | Salt, oil, acid, spices |
Are Long-Lasting Pickles Safe to Eat?
Yes, when prepared traditionally and stored properly.
- Natural ingredients
- Safe for regular consumption (in moderation)
Proven through generations
Always check for spoilage signs like unusual smell, mold, or excessive moisture.
Final Thoughts
Shelf life also depends on how pickles are stored.
Best practice
Pickles last longer than other foods not by accident – but by design. The perfect combination of salt, oil, acidity, spices, and tradition creates one of the most effective natural preservation systems in the world.That’s why pickles remain a staple across generations.
- Airtight containers
- Clean, dry spoons
- No moisture contamination
- Storage away from sunlight
When followed correctly, pickles remain safe and tasty for extended periods.
